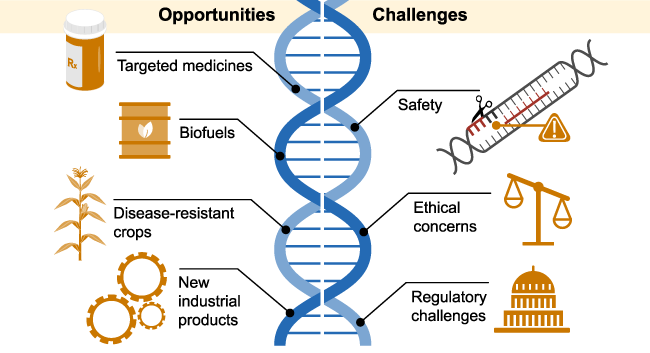
ISDRA2TnpB: A New Tool for Better Plant Editing
In the world of biotechnology, scientists are always looking for new ways to improve plants. One of the latest discoveries is ISDRA2TnpB, a new tool that helps make precise changes to plant genes. This tool has the potential to create crops that are more resilient to diseases, pests, and environmental challenges, and can also boost their nutritional value.
What is ISDRA2TnpB?
ISDRA2TnpB is a new way to edit plant genes. It uses special DNA pieces called transposons, which are sometimes known as “jumping genes” because they can move around within a plant’s DNA. Unlike other gene-editing tools like CRISPR, which need a specific guide to find the right spot in the DNA, ISDRA2TnpB works by using these transposons to make changes directly.
This makes ISDRA2TnpB a simpler and potentially more flexible tool for modifying plant genes, which could help scientists develop plants with desirable traits more easily.
How Does ISDRA2TnpB Work?
ISDRA2TnpB uses a protein called TnpB to make precise cuts in the DNA of plants. This allows scientists to either add new genes, remove unwanted ones, or adjust how certain genes work. Here’s what it can do:
- Add Useful Genes: Scientists can insert genes that help plants resist drought or pests.
- Remove Problematic Genes: They can delete genes that make plants susceptible to diseases.
- Adjust Gene Activity: They can change the parts of the DNA that control how genes are turned on or off, making plants better at handling different environmental conditions.
How Can ISDRA2TnpB Be Used?
ISDRA2TnpB could be a game-changer in many areas of agriculture. Here’s how it might be used:
1. Better Crops
Scientists could use ISDRA2TnpB to create crops that produce more food or have better nutritional value. This means higher yields and healthier food.
2. Disease-Resistant Plants
ISDRA2TnpB could help develop plants that are more resistant to diseases, reducing the need for chemicals and keeping crops healthier.
3. Pest-Resistant Crops
By making plants naturally resistant to insects and other pests, ISDRA2TnpB could cut down the need for pesticides, which is better for the environment.
4. Nutritional Boost
ISDRA2TnpB can be used to increase the levels of vitamins and minerals in plants, which can help fight malnutrition, especially in developing countries.
5. Adapting to Climate Change
Climate change affects weather patterns and can make farming more difficult. ISDRA2TnpB can help create plants that can survive tough conditions like droughts or high temperatures.
Why ISDRA2TnpB is Special
ISDRA2TnpB has some advantages over other tools like CRISPR:
Flexibility: It doesn’t need a specific guide to target DNA, making it easier to use for different types of gene editing.
Simplicity: The TnpB protein makes it easier to target DNA and make changes.
Fewer Mistakes: Because it doesn’t use guides like CRISPR, there’s less chance of accidentally altering the wrong part of the DNA.
Effective Editing: It’s great at adding or removing specific genes, which is perfect for making precise changes.
Challenges and What’s Next
While ISDRA2TnpB shows a lot of promise, there are still some challenges. One issue is making sure the changes it makes stay stable in future generations of plants. Also, regulations and public opinion on genetic modifications are still developing, which could affect how widely ISDRA2TnpB is used.
Despite these challenges, ISDRA2TnpB is likely to become an important tool in agriculture. Its ability to make precise and flexible changes to plant genes could help develop crops that are more resilient, nutritious, and sustainable.
